


Did you know that 94% of employees reported that they would stay at a company longer if it invested in continuous learning opportunities, according to Linkedln”s 2018 Workplace Learning Report?
The ascent of digital technology is revamping the landscape of talent development. Traditional modes of learning are being reshaped by online platforms, virtual classrooms, and interactive tools that offer personalized and flexible learning experiences. E-learning modules, virtual simulations, and AI-driven assessments are optimizing skill acquisition and performance evaluation. This digital transformation enables learners to access a wealth of knowledge anytime, anywhere, bringing forth continuous growth and adaptability in an increasingly dynamic professional world. On this front, a learning management system (LMS) is of paramount importance.
An LMS functions as a software application facilitating the creation, delivery, and automation of learning and training materials. These programs contribute to the digitalization of the learning journey by integrating essential components such as learning content, content creation, collaboration, tracking, and reporting tools into a cohesive platform.
An LMS is capable of making learning a part of the work routine, which is particularly beneficial when 68% of employees prefer to learn at work, as per the 2018 Workplace Learning Report. Also, 58% of employees prefer to learn at their own pace, which can also be enabled by LMS. Organizations employing LMS establish a contemporary and efficient learning atmosphere tailored to the demands of the hybrid workplace.
Content Creation and Management
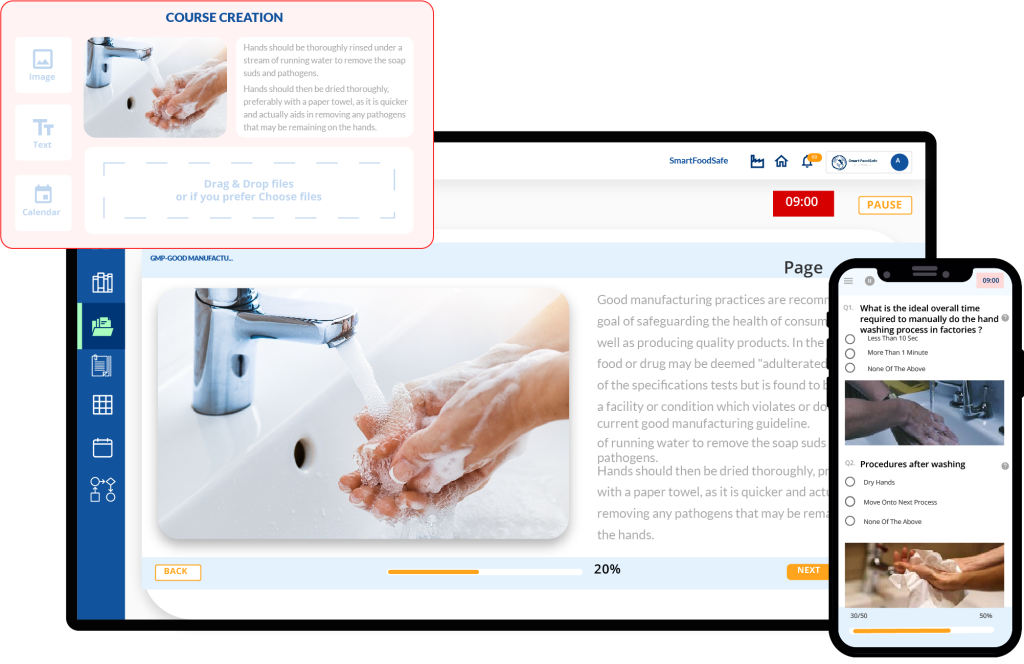
The process begins with content creation. Educators, trainers, or administrators create digital learning materials to be organized and uploaded into the LMS system. Courses can be kept engaging by including audio files, video files, presentations, interactive quizzes, virtual reality, and more.
User Management
The LMS allows administrators to manage user accounts. This includes creating new accounts, enrolling users in specific courses, assigning roles (such as student, instructor, or administrator), and setting access permissions.
Course Creation and Structuring
Instructors or content creators use the LMS to create courses. A course typically consists of a sequence of modules or lessons. Within these modules, they can upload content, set objectives, and define learning outcomes. They can also create assessments like quizzes or assignments to evaluate learners’ progress.
Enrollment and Access
Learners or students are enrolled in courses by administrators or instructors. Once enrolled, they gain access to the course materials and resources within the LMS. Some LMS platforms allow for self-enrollment, where learners can choose and enroll in courses on their own.
Learning Delivery
Administrators can share the created lessons with employees online and keep track of their progress. Learners access the course materials, which can include videos, presentations, reading materials, interactive simulations, and more, through the LMS. They can study at their own pace, following the course structure set by the instructor. Learners can then complete assessments, and the system automatically grades and records their performance.
Progress Tracking
Progress tracking features allow responsible parties to oversee learners’ advancement through the course. Certain systems even offer advanced reports that managers can view within dashboards to monitor the progress of each learner’s journey. This simplifies the process of demonstrating compliance and remaining prepared for significant audits.
Communication and Collaboration
LMS platforms often include communication tools like discussion forums, chat, and messaging systems. These tools facilitate interaction between learners and instructors, enabling discussions, asking questions, and seeking clarifications.
Feedback and Reporting
Instructors can provide feedback on assignments and assessments through the LMS. Additionally, administrators and instructors can access detailed reports and analytics about learner progress, engagement, and performance. This information helps them refine courses and instructional strategies.
Certification and Completion
When a training course is successfully completed, the learner can receive a certificate and proof of competencies, which are credentials that can be shared on resumes and professional profiles. When a learner completes a course, managers receive corresponding notifications to ensure that everyone is well-informed.
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.
The impact of labor quality and digitalization on upgrading the industrial structure of Asian economies was explored in a study that encompassed 32 Asian countries over the time period from 2010–2021.
The study’s findings revealed that a high-quality workforce positively affects elevating the industrial structure, with digitalization also playing a crucial role by enhancing connectivity, fostering collaboration, and increasing productivity. It further indicated that Asian countries should prioritize investments in education and skill development to refine the quality of their human capital while implementing policies that facilitate digitalization, including investments in digital infrastructure, the development of digital skills, and the establishment of a supportive regulatory environment. By doing so, Asian countries can accelerate the upgradation of their industries, leading to sustainable economic growth, boosted competitiveness, and improved living standards.
The upgradation of industrial structure refers to the process of strengthening and advancing existing industrial infrastructure within a specific sector or region. This involves the modernization and improvement of various aspects of industrial operations, including technology, processes, equipment, and overall efficiency, with the aim of fostering economic expansion and competency. Industrial transformation can be multi-faceted, encompassing dimensions such as technological advancement, infrastructure development, skill enrichment, and research and development efforts. Developing economies, like the majority of the countries in Asia, face substantial challenges in upscaling their industrial structures, making it a matter of great concern. A skilled workforce adept at new technologies drives progress by efficiently operating machinery, maintaining quality standards, and contributing to research and development. This interplay between technology and workforce quality preserves a thriving industrial landscape.
Throughout the last four decades, many economies in Asia have undergone considerable structural changes in their output and employment systems. The East Asian economies, including Japan and Southeast Asian countries, witnessed notable economic and industrial advancements, while India aimed to boost manufacturing’s GDP contribution and job creation, and the Philippines attempted to reverse a long period of deindustrialization. The pivotal role of the industrial sector in Asian economies’ rapid growth underscores the necessity of understanding the interlinking between labor quality, digitalization, and industrial upgrading, all of which are crucial for sustaining and fortifying economic development.
Assessing Labor Quality and Digitalization in Asian Nations
The study “Unleashing the horizons of labor quality, digitalization on upgradation of industrial structure in Asian economies” sheds light on the intricate relationship between labor quality, digitalization, and industrial structure upgrading across the diverse landscape of Asian countries. Despite the surge in economic growth and industrialization, these dimensions have received limited attention in previous research, making this study a significant contribution.
The study employed panel data from 32 Asian countries spanning 2010 to 2021. By acknowledging the diversity within labor markets, encompassing various levels of education, skills, and expertise, the research offers insights into the potential impact of labor quality on industrial advancement.
Investing in Human Capital for Industrial Transformation
In theoretical terms, the augmentation of human capital quality emerges as a pivotal factor in shaping the industrial structure. The study reveals a strong positive correlation between labor quality and industrial framework advancement across different Asian nations. Given the heterogeneous nature of labor markets in these countries, strategic investments in human capital through educational initiatives, skill development, and workforce training emerge as catalysts for prompting industrial productivity and efficiency. This emphasis on refining labor quality contributes substantively to the overall enhancement of the industrial structure, upholding economic growth, investment appeal, and an environment conducive to progress.
Digitalization’s Transformative Outcome on Industrial Landscape
The study further highlights the noteworthy and favorable influence of digitalization on the evolution of the industrial landscape in Asian countries. This wave of digital transformation stimulates the advancement of industrial structure, underpinned by strong institutional frameworks, comprehensive employment strategies, and vigorous research and development endeavors. The integration of digital technologies like automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics has fundamentally reshaped industry dynamics in Asian economies. This integration translates to increased productivity, operational efficiency, and innovative capabilities, bolstering these industries’ competitive positions globally.
Policy Implications for Sustainable Industrial Development
The implications of these findings extend profoundly to policy formulation. Governments in Asian nations are encouraged to recognize the pivotal roles of labor quality and digitalization in driving industrial transformation. Policy frameworks should prioritize investments in education, skill enrichment, and digital infrastructure to nurture a skilled workforce and foster technological innovation. Such measures can catalyze industrial expansion, enhance global competitiveness, and support sustainable development trajectories. Facilitating knowledge exchange and collaboration among nations can further facilitate the transfer of skills, technological expertise, and insights, fostering mutual learning and paving the way for cohesive regional industrial integration.
Conclusion and Future Research
In the pursuit of efficacious developmental strategies and pathways, each Asian country should meticulously evaluate its unique strengths and weaknesses against the backdrop of digitalization. To address the digital divide prevalent in certain Central and South Asian nations with less advanced technological landscapes, a concerted effort is needed to bolster regional infrastructure. A strategic emphasis on cultivating specialized talent, reinforcing digital technology-focused research and development funding, and creating an innovation-friendly ecosystem is essential for these countries.
Strategic investments in human capital development and a wholehearted embrace of digitalization and technological progress yield dividends in the form of heightened productivity, efficiency, innovation, and global competitiveness. These insights furnish invaluable guidance for policymakers, industry stakeholders, and researchers in their endeavors to propel sustainable industrial development and economic prosperity within the region.
Embracing insights from the study, one practical approach for Asian industries is combining digitalization and skill development through the adoption of an efficient Learning Management System (LMS). It presents as a game-changer to revolutionize workforce training strategies by facilitating the seamless integration of digital features.
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern business, staying ahead requires more than just keeping up with the latest trends – it demands a workforce that is agile, well-equipped, and empowered to drive growth. This is where Smart Training, a cutting-edge learning management system, comes into play. By harnessing the power of digitalization, Smart Training offers a profound approach to workforce development, ensuring your company remains at the forefront of your industry’s evolution.
In a world where digitalization shapes the competitive landscape, Smart Training stands as a beacon of innovation by leveraging its capabilities to empower its workforce, drive industry transformation, and secure a prosperous
Did you know that 94% of employees reported that they would stay at a company longer if it invested in continuous learning opportunities, according to Linkedln”s 2018 Workplace Learning Report?
The ascent of digital technology is revamping the landscape of talent development. Traditional modes of learning are being reshaped by online platforms, virtual classrooms, and interactive tools that offer personalized and flexible learning experiences. E-learning modules, virtual simulations, and AI-driven assessments are optimizing skill acquisition and performance evaluation. This digital transformation enables learners to access a wealth of knowledge anytime, anywhere, bringing forth continuous growth and adaptability in an increasingly dynamic professional world. On this front, a learning management system (LMS) is of paramount importance.
An LMS functions as a software application facilitating the creation, delivery, and automation of learning and training materials. These programs contribute to the digitalization of the learning journey by integrating essential components such as learning content, content creation, collaboration, tracking, and reporting tools into a cohesive platform.
An LMS is capable of making learning a part of the work routine, which is particularly beneficial when 68% of employees prefer to learn at work, as per the 2018 Workplace Learning Report. Also, 58% of employees prefer to learn at their own pace, which can also be enabled by LMS. Organizations employing LMS establish a contemporary and efficient learning atmosphere tailored to the demands of the hybrid workplace.
Content Creation and Management
The process begins with content creation. Educators, trainers, or administrators create digital learning materials to be organized and uploaded into the LMS system. Courses can be kept engaging by including audio files, video files, presentations, interactive quizzes, virtual reality, and more.
User Management
The LMS allows administrators to manage user accounts. This includes creating new accounts, enrolling users in specific courses, assigning roles (such as student, instructor, or administrator), and setting access permissions.
Course Creation and Structuring
Instructors or content creators use the LMS to create courses. A course typically consists of a sequence of modules or lessons. Within these modules, they can upload content, set objectives, and define learning outcomes. They can also create assessments like quizzes or assignments to evaluate learners’ progress.
Enrollment and Access
Learners or students are enrolled in courses by administrators or instructors. Once enrolled, they gain access to the course materials and resources within the LMS. Some LMS platforms allow for self-enrollment, where learners can choose and enroll in courses on their own.
Learning Delivery
Administrators can share the created lessons with employees online and keep track of their progress. Learners access the course materials, which can include videos, presentations, reading materials, interactive simulations, and more, through the LMS. They can study at their own pace, following the course structure set by the instructor. Learners can then complete assessments, and the system automatically grades and records their performance.
Progress Tracking
Progress tracking features allow responsible parties to oversee learners’ advancement through the course. Certain systems even offer advanced reports that managers can view within dashboards to monitor the progress of each learner’s journey. This simplifies the process of demonstrating compliance and remaining prepared for significant audits.
Communication and Collaboration
LMS platforms often include communication tools like discussion forums, chat, and messaging systems. These tools facilitate interaction between learners and instructors, enabling discussions, asking questions, and seeking clarifications.
Feedback and Reporting
Instructors can provide feedback on assignments and assessments through the LMS. Additionally, administrators and instructors can access detailed reports and analytics about learner progress, engagement, and performance. This information helps them refine courses and instructional strategies.
Certification and Completion
When a training course is successfully completed, the learner can receive a certificate and proof of competencies, which are credentials that can be shared on resumes and professional profiles. When a learner completes a course, managers receive corresponding notifications to ensure that everyone is well-informed.
Boost your food business’s hygiene standards with Smart Food Safe’s tech-driven solutions—streamline 4C processes to yield optimal results, and ensure compliance effortlessly.

The impact of labor quality and digitalization on upgrading the industrial structure of Asian economies was explored in a study that encompassed 32 Asian countries over the time period from 2010–2021.
The study’s findings revealed that a high-quality workforce positively affects elevating the industrial structure, with digitalization also playing a crucial role by enhancing connectivity, fostering collaboration, and increasing productivity. It further indicated that Asian countries should prioritize investments in education and skill development to refine the quality of their human capital while implementing policies that facilitate digitalization, including investments in digital infrastructure, the development of digital skills, and the establishment of a supportive regulatory environment. By doing so, Asian countries can accelerate the upgradation of their industries, leading to sustainable economic growth, boosted competitiveness, and improved living standards.
The upgradation of industrial structure refers to the process of strengthening and advancing existing industrial infrastructure within a specific sector or region. This involves the modernization and improvement of various aspects of industrial operations, including technology, processes, equipment, and overall efficiency, with the aim of fostering economic expansion and competency. Industrial transformation can be multi-faceted, encompassing dimensions such as technological advancement, infrastructure development, skill enrichment, and research and development efforts. Developing economies, like the majority of the countries in Asia, face substantial challenges in upscaling their industrial structures, making it a matter of great concern. A skilled workforce adept at new technologies drives progress by efficiently operating machinery, maintaining quality standards, and contributing to research and development. This interplay between technology and workforce quality preserves a thriving industrial landscape.
Throughout the last four decades, many economies in Asia have undergone considerable structural changes in their output and employment systems. The East Asian economies, including Japan and Southeast Asian countries, witnessed notable economic and industrial advancements, while India aimed to boost manufacturing’s GDP contribution and job creation, and the Philippines attempted to reverse a long period of deindustrialization. The pivotal role of the industrial sector in Asian economies’ rapid growth underscores the necessity of understanding the interlinking between labor quality, digitalization, and industrial upgrading, all of which are crucial for sustaining and fortifying economic development.
Assessing Labor Quality and Digitalization in Asian Nations
The study “Unleashing the horizons of labor quality, digitalization on upgradation of industrial structure in Asian economies” sheds light on the intricate relationship between labor quality, digitalization, and industrial structure upgrading across the diverse landscape of Asian countries. Despite the surge in economic growth and industrialization, these dimensions have received limited attention in previous research, making this study a significant contribution.
The study employed panel data from 32 Asian countries spanning 2010 to 2021. By acknowledging the diversity within labor markets, encompassing various levels of education, skills, and expertise, the research offers insights into the potential impact of labor quality on industrial advancement.
Investing in Human Capital for Industrial Transformation
In theoretical terms, the augmentation of human capital quality emerges as a pivotal factor in shaping the industrial structure. The study reveals a strong positive correlation between labor quality and industrial framework advancement across different Asian nations. Given the heterogeneous nature of labor markets in these countries, strategic investments in human capital through educational initiatives, skill development, and workforce training emerge as catalysts for prompting industrial productivity and efficiency. This emphasis on refining labor quality contributes substantively to the overall enhancement of the industrial structure, upholding economic growth, investment appeal, and an environment conducive to progress.
Digitalization’s Transformative Outcome on Industrial Landscape
The study further highlights the noteworthy and favorable influence of digitalization on the evolution of the industrial landscape in Asian countries. This wave of digital transformation stimulates the advancement of industrial structure, underpinned by strong institutional frameworks, comprehensive employment strategies, and vigorous research and development endeavors. The integration of digital technologies like automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics has fundamentally reshaped industry dynamics in Asian economies. This integration translates to increased productivity, operational efficiency, and innovative capabilities, bolstering these industries’ competitive positions globally.
Policy Implications for Sustainable Industrial Development
The implications of these findings extend profoundly to policy formulation. Governments in Asian nations are encouraged to recognize the pivotal roles of labor quality and digitalization in driving industrial transformation. Policy frameworks should prioritize investments in education, skill enrichment, and digital infrastructure to nurture a skilled workforce and foster technological innovation. Such measures can catalyze industrial expansion, enhance global competitiveness, and support sustainable development trajectories. Facilitating knowledge exchange and collaboration among nations can further facilitate the transfer of skills, technological expertise, and insights, fostering mutual learning and paving the way for cohesive regional industrial integration.
Conclusion and Future Research
In the pursuit of efficacious developmental strategies and pathways, each Asian country should meticulously evaluate its unique strengths and weaknesses against the backdrop of digitalization. To address the digital divide prevalent in certain Central and South Asian nations with less advanced technological landscapes, a concerted effort is needed to bolster regional infrastructure. A strategic emphasis on cultivating specialized talent, reinforcing digital technology-focused research and development funding, and creating an innovation-friendly ecosystem is essential for these countries.
Strategic investments in human capital development and a wholehearted embrace of digitalization and technological progress yield dividends in the form of heightened productivity, efficiency, innovation, and global competitiveness. These insights furnish invaluable guidance for policymakers, industry stakeholders, and researchers in their endeavors to propel sustainable industrial development and economic prosperity within the region.
Embracing insights from the study, one practical approach for Asian industries is combining digitalization and skill development through the adoption of an efficient Learning Management System (LMS). It presents as a game-changer to revolutionize workforce training strategies by facilitating the seamless integration of digital features.
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern business, staying ahead requires more than just keeping up with the latest trends – it demands a workforce that is agile, well-equipped, and empowered to drive growth. This is where Smart Training, a cutting-edge learning management system, comes into play. By harnessing the power of digitalization, Smart Training offers a profound approach to workforce development, ensuring your company remains at the forefront of your industry’s evolution.
In a world where digitalization shapes the competitive landscape, Smart Training stands as a beacon of innovation by leveraging its capabilities to empower its workforce, drive industry transformation, and secure a prosperous

Signup to receive latest news, insights and updates on training management